Science
SpaceX's Starship Aces Key Engine Test Towards Safe Moon Landing For Astronauts
- Starship is SpaceX's next-generation system designed for deep-space exploration.
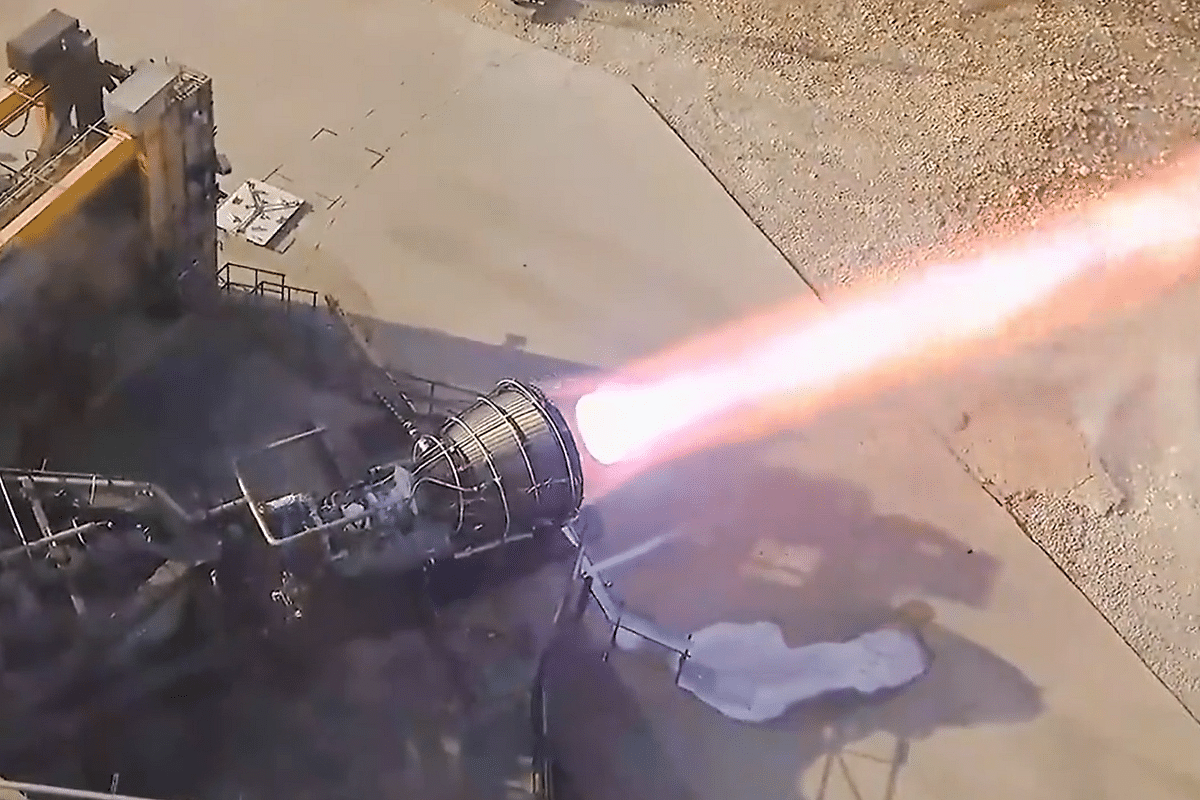
Videograb of the Raptor vacuum engine test
SpaceX recently conducted a test-firing of its Starship engines in cold lunar-like conditions as part of the preparations for a future human Moon landing.
The successful "cold engine" start demonstrated that the company's Raptor engine can be restarted in space after leaving Earth, ensuring the safe transportation of astronauts to the Moon's surface.
NASA officials shared this update in a blog post, noting that SpaceX is aiming to bring the Artemis 3 crew to the Moon with Starship in 2025 or 2026.
In a video shared on X, SpaceX showcased the firing of a steaming-cold Raptor engine at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Alabama.
The brief three-second firing demonstrated the power and functionality of the engine.
Starship is SpaceX's next-generation system designed for deep-space exploration. While it has not yet been launched into space, SpaceX made a significant milestone in April by successfully launching a fully stacked Starship.
However, the launch encountered several issues, resulting in the rocket spinning out of control, being remotely detonated, and causing debris to scatter in the surrounding area.
Despite these setbacks, SpaceX continues to refine and improve the Starship system in pursuit of its ambitious space exploration goals.
Elon Musk has indicated that a new Starship launch could happen quickly, and the US Federal Aviation Administration's recent comments suggest that SpaceX may receive a licence for a launch attempt in October.
NASA officials have expressed confidence in SpaceX's progress towards meeting its Artemis 3 obligations after a successful Raptor engine test.
In a blog post, agency officials stated that these tests provide early validation of the systems necessary for lunar surface missions and that data reviews are continually increasing NASA's confidence in the readiness of the US industry for the mission.
In November 2021, SpaceX achieved a significant milestone for the Raptor engine, demonstrating its ability to fire for the required duration of 281 seconds (4.5 minutes) for the long descent to the Moon.
The engine also adjusted its power level during testing to meet agency requirements. SpaceX released footage of this test, showcasing the engine's capabilities.
NASA has indicated that it is prepared to launch Artemis 3 even if Starship is not ready for a Moon landing in 2025 or 2026.
The agency could proceed with Artemis 3 without a Moon landing and instead fly an alternate mission with a crew.
The plan would involve using Starship for a future mission, such as Artemis 4, which would mark the first human lunar landing since Apollo 17 in 1972.
NASA is seeking multiple successful launches by Starship before authorising a lunar landing with astronauts, among other milestones.
Artemis 1 involved an uncrewed NASA Orion spacecraft orbiting the Moon in late 2022. It was launched there using the agency's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket.
Artemis 2 is scheduled to take place no earlier than November 2024. For Artemis 2, three NASA astronauts and a Canadian will be sent around the Moon using the SLS and Orion.
SpaceX is not the sole vendor responsible for transporting humans to the Moon for NASA missions.
In May 2023, a consortium led by Blue Origin also became eligible to bid for missions after Artemis 4.
Support Swarajya's 50 Ground Reports Project & Sponsor A Story
Every general election Swarajya does a 50 ground reports project.
Aimed only at serious readers and those who appreciate the nuances of political undercurrents, the project provides a sense of India's electoral landscape. As you know, these reports are produced after considerable investment of travel, time and effort on the ground.
This time too we've kicked off the project in style and have covered over 30 constituencies already. If you're someone who appreciates such work and have enjoyed our coverage please consider sponsoring a ground report for just Rs 2999 to Rs 19,999 - it goes a long way in helping us produce more quality reportage.
You can also back this project by becoming a subscriber for as little as Rs 999 - so do click on this links and choose a plan that suits you and back us.
Click below to contribute.
Latest